Physical Address
Block 308 DBM Plaza, Wuse Zone 1, Abuja, Nigeria
+2347062940253
Physical Address
Block 308 DBM Plaza, Wuse Zone 1, Abuja, Nigeria
+2347062940253
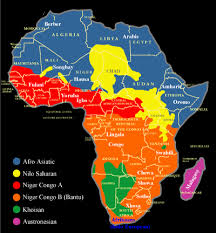
Africa hosts over 2,000 languages from major families like Niger-Congo (Swahili, Yoruba, Igbo, Bantu) and Afro-Asiatic (Arabic, Hausa, Amharic), alongside Nilo-Saharan and Khoisan, reflecting thousands of distinct ethnic groups and rich cultures, with colonial languages like English and French also prevalent. Major tribes and their tongues include the Zulu (Zulu), Xhosa (Xhosa) in South Africa, the Hausa (Hausa) in West Africa, and the Oromo (Oromo) in Ethiopia, each with unique cultural identities tied to their language.
Major Language Families & Examples
Major Ethnic Groups & Languages
Key Takeaway
Africa’s linguistic landscape is incredibly diverse, with thousands of native tongues tied to unique ethnic identities, alongside influential colonial languages used in government and education, such as English, French, and Portuguese
Africa is a continent of immense cultural and linguistic diversity, home to an estimated 1,500 to 2,000 distinct languages and thousands of ethnic groups. These groups range from nomadic pastoralists to highly urbanized societies, each contributing to a rich tapestry of heritage.
Major Language Families
African languages are generally classified into four primary linguistic phyla:
Notable Ethnic Groups and Their Languages
| Ethnic Group | Region | Primary Language | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hausa | West Africa | Hausa | The largest ethnic group in Africa, with 78 million people; language is a major lingua franca in trade. |
| Yoruba | West Africa | Yoruba | Highly urbanized society with a rich creation myth; significant diaspora in the Americas. |
| Zulu | Southern Africa | isiZulu | Known historically as a warrior nation under Shaka Zulu; isiZulu is the most spoken home language in South Africa. |
| Oromo | Horn of Africa | Afaan Oromo | The largest group in Ethiopia; historically used the gada system, a form of democratic government. |
| Berber (Amazigh) | North Africa | Berber (Tamazight) | Indigenous to North Africa since 3000 BCE; primarily farmers and pastoralists. |
| Igbo | West Africa | Igbo | From Southern Nigeria; known for a decentralized traditional political structure and strong trading culture. |
Most Spoken Languages in 2025
According to data from Altezza Travel and Britannica, the languages with the highest number of speakers (including native and second-language users) include:
Yoruba: 40–45 million speakers.
Swahili: Over 230 million speakers. It serves as a lingua franca across East and Central Africa.
Arabic: Approximately 213.5 million speakers. It has the largest number of native speakers on the continent.
Hausa: Up to 70 million speakers. It is the most widely spoken language in West Africa.
Amharic: Up to 60 million speakers. It uses a unique ancient script with over 270 symbols.
Cultural & Tribal Overviews
World Atlas | Languages Spoken in Africa
Provides ranked lists of languages by native speaker count, covering major tongues like Arabic, Amharic, and Yoruba.
Africa Guide | African Tribes
This resource features sub-pages for dozens of major groups, including the Ashanti, Maasai, Tuareg, and Zulu, focusing on their specific customs and traditional homelands.
African Studies Association (ASA)
The ASA is the largest global organization dedicated to the exchange of information about Africa, providing access to scholarly research and contemporary cultural data.